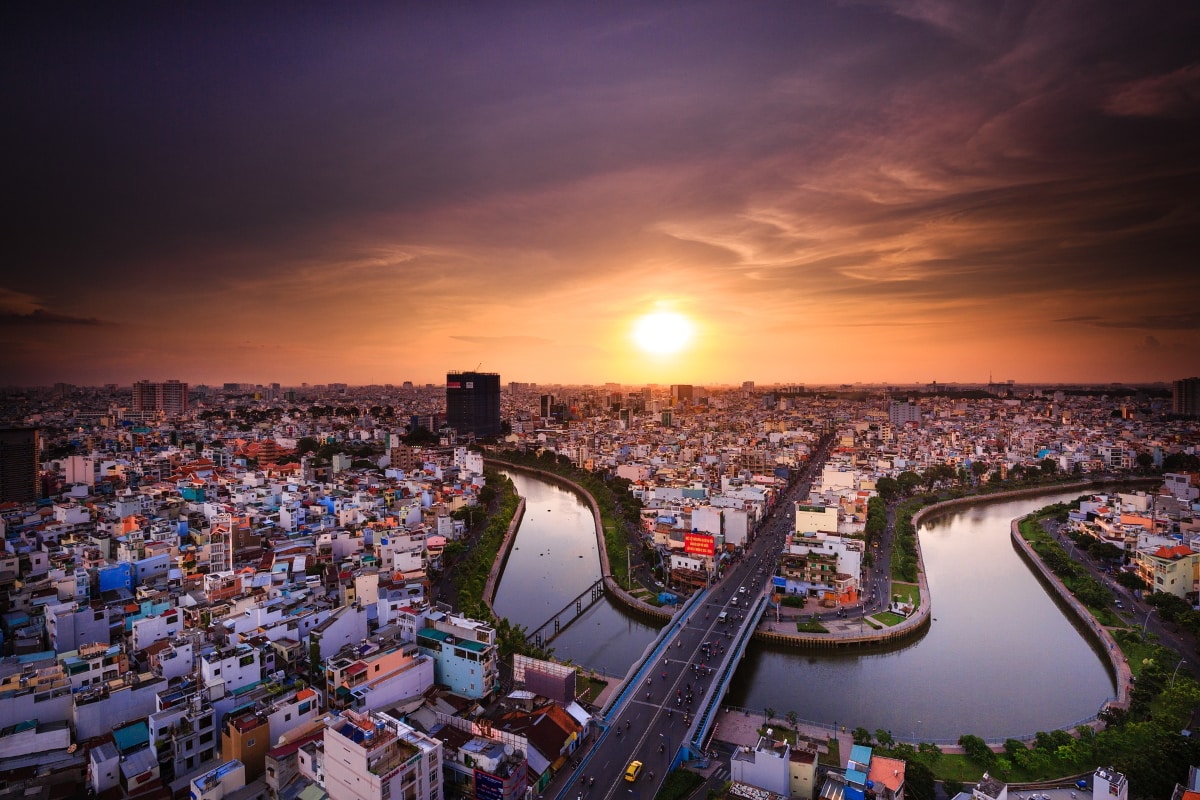
Vietnam Economy
Vietnam’s economy has shifted from a centrally-planned economy to a market economy with rapid growth over the last three decades. In 2018, the Vietnam economy expanded at a rate of 6.5%. The country’s nominal GDP reached over $241 billion, tripling compared to ten years before. The IMF predicts that Vietnam’s GDP will grow steadily at 6.5% annually for the next five years.

Vietnam: a lower middle-income country
After economic and political reform in 1986 led by Đổi Mới, Vietnam has transformed itself from one of the poorest countries in the world to a lower middle-income country. Last year, Vietnam’s GDP per capita (PPP) was $7,482. The middle class in Vietnam accounts for 13% of the population.

The unemployment rate of Vietnam has been stable at 2.2% since last year. The trend will continue for the next five years.
Currency and central bank
The Vietnamese dong is the official currency of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam. It is one of the highest-denominated currencies. Currently, one U.S. dollar equals around 23,000 Vietnamese dong. The currency is loosely pegged to the U.S. dollar, allowing the exchange rate to adjust gradually along with change in the market.
The dong is issued by Vietnam’s central bank, the State Bank of Vietnam (SBV). Along with printing currency, the Vietnamese central bank’s main objectives include maintaining monetary stability through monetary policies, supervising financial institutions, managing the country’s international reserves, and issuing government bonds. The SBV holds 65% stocks of VietinBank, the largest listed bank by market capitalisation.
Vietnam economy: hyperinflation from 1987 to 1992
During Vietnam’s early years of reformation, the country experienced hyperinflation from 1987 to 1992. However, Vietnam’s economy has since recovered and its inflation rate stood at 4% in 2018. The Vietnamese government has set the same inflation target of 4% for this year.
Industry and trade
Vietnam’s economy is highly driven by the services sector, which accounts for about 44% of the country’s GDP. Industry and agriculture contribute 39% and 15% of Vietnam’s GDP respectively.
The main industries in Vietnam are electronics, food processing, wood, textiles, footwear and tourism. The country is also the biggest producer of robusta beans and the second-largest coffee exporter in the world. Some of Vietnam’s largest firms include VietinBank, oil and gas company Petrolimex, and dairy factory Vinamilk.
Many foreign companies, especially from Japan and South Korea, set up their manufacturing plants in Vietnam due to the low cost of labour. For example, Samsung produces 40% of its phones in Vietnam.
Trade and Competitiveness
Vietnam’s trade balance has maintained a surplus for the last three years. In 2018, Vietnam recorded a trade surplus of $6.8 billion. Total exports were up 13.2% from the previous year, to $243.5 billion, while imports reached $236.7 billion.
About one-fifth of Vietnam’s total exports go to the U.S. Meanwhile, imports from East Asian countries such as China, Japan and South Korea, are equivalent to more than half of total Vietnam imports.
Disbursed FDI in Vietnam rose by 9.1% in 2018 to $19.1 billion. About 47% of foreign investment targeted the manufacturing and processing sectors. The real estate sector ranked second, followed by the retail sector. The biggest investments came from Japan, South Korea and Singapore.
On the Ease of Doing Business index published by the World Bank, Vietnam came in 69th position. It also ranked 67th in the Global Competitiveness Report by the World Economic Forum – an improvement of 10 places compared to 2018.
Stock exchanges and capital markets
Vietnam has two stock exchanges: the Ho Chi Minh Stock Exchange (HOSE) and Hanoi Stock Exchange (HNX). The HOSE was established in 1998 and HNX was founded in 2009.
In total, there are 377 companies in HOSE and 376 listed companies in HNX. The HOSE is the main market for state-owned companies and accounted for 93% of total market capitalisation in both exchanges, which reached $131 billion at the end of 2018. HNX, on the other hand, focuses on small and medium-sized enterprises.
Main indices of Vietnam stock exchanges are the VN30 and the VN-Index. These indices include blue chips such as Vietcombank, Vinamik, Vingroup, Vietjet and Masan. Other indices include VNMID Index, VNSML Index, VN100 and VNALL Index.
Investment Regulation
Foreign ownership in Vietnamese companies is currently limited to 49% in general. The limit is lower in some sectors, such as in banking and aviation. The telecommunication services threshold ranges from 30% to 51%.
Foreign investment in certain projects can receive incentives, such as lower tax rates, import duty exemption for fixed assets, and reduction or exemption of land rental. Business lines eligible for incentives include technology, energy, textiles, agriculture and healthcare.










 Australia
Australia China
China India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Japan
Japan Malaysia
Malaysia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam
 Germany
Germany Hong Kong
Hong Kong USA
USA Switzerland
Switzerland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom











