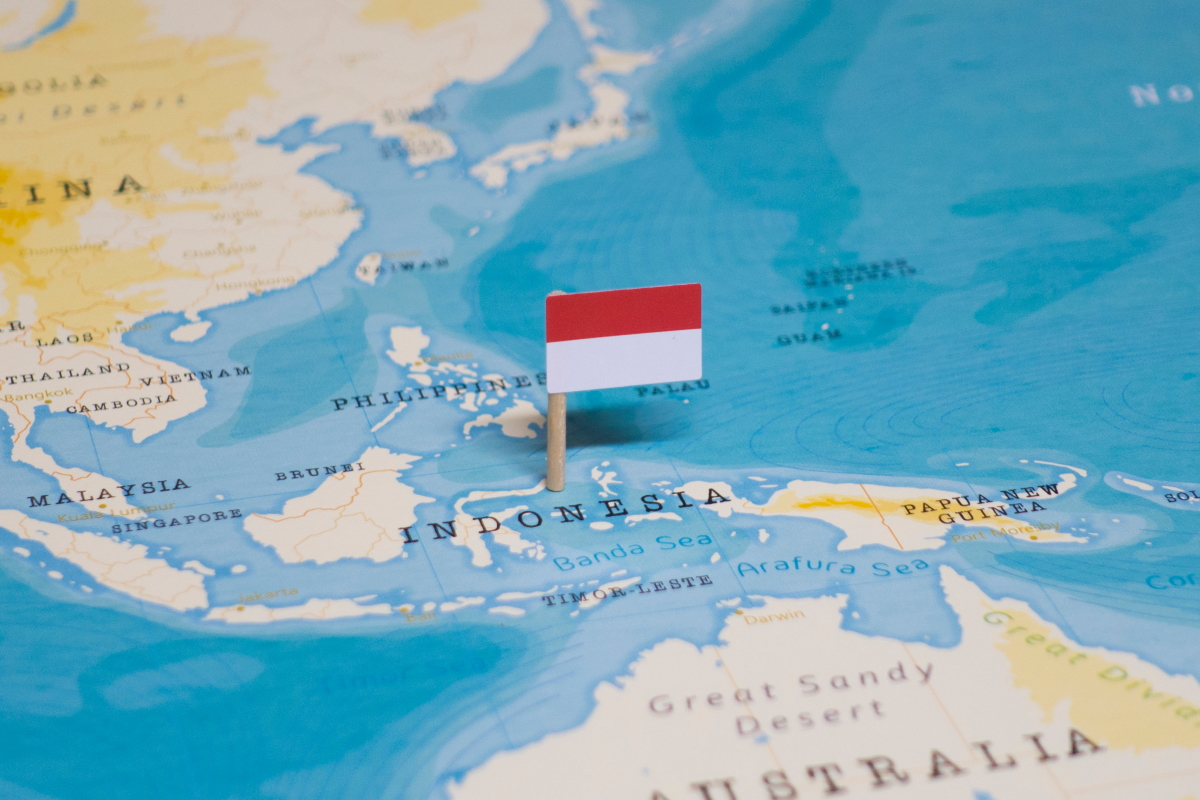
Among the world’s top emerging markets, Indonesia posted a 3.69% growth in gross domestic product (GDP) for 2021, reversing course from a 2.07% contraction a year earlier due to pandemic-induced shutdowns.
Pegged as Southeast Asia’s largest economy, Indonesia’s GDP growth figure is just shy of the finance ministry forecast of 3.7%. While there seem to be no big surprises, the country still faces headwinds from a surging coronavirus.
After posting the decade’s first recession in 2020, Indonesia recovered economic losses in 2021 largely thanks to a growth of 2.02% in domestic consumption, which makes up over half of the country’s GDP. Growth in Indonesia’s economy was aided by easing containment measures, strong government support, and gains in exports due to rising commodity prices.
However, Indonesia is still far from achieving its pre-pandemic GDP growth rate of over 5%.
Upside risk of prices and rising inflation
High liquidity due to government stimulus in world economies during the pandemic helped businesses stay afloat, but rising demand is now adding to inflation.
Oxford Economics in a recent report said that Indonesia’s CPI index rose 2.1% year-on-year in February, lower than 2.2% the month before. However, the country’s core inflation rose to 2% from 1.8% during the same period. More notably, energy inflation widened to 1.2% from 0.2%.
Oxford’s Senior Economist Sung Eun Jung says that rising core inflation indicates an improving demand, and the ongoing Russia and Ukraine war is likely to put pressure on food and energy prices. Russia is the world’s second-largest oil supplier.
The core inflation of Indonesia has been on the rise for five consecutive months and is likely to go higher due to the geopolitical issues in Europe. ING in a recent report said that it expects headline and core inflation to heat up, forecasting a full-year inflation rate of 3.4%.
Central banks globally have taken a hawkish stance on key interest rates in 2022. ING expects Bank Indonesia to revise its key interest rates by the second quarter of 2022, stemming from a faster inflation rate and a weaker currency. Oxford Economics forecasts Bank Indonesia to tighten its policy rate by 75bps this year.
Industries driving Indonesia’s recovery
Although Covid-19 remains a risk, Indonesian equities will likely see a jump in 2022 due to structural economic recovery while fixed income assets may show muted performance due to policy tightening, writes Schroders.
The asset management firm sees pent-up demand to increase inflation and disrupt supply chains. It sees consumption and investments to drive the economic recovery in Indonesia as Covid-19 wanes.
Schroders’ Macro & Market Outlook 2022 expects that the mid-to-high end consumer segment will drive consumption recovery while middle-low would prioritize savings. The base metal industry in the country would continue to see higher investments as demand for electric vehicles and batteries increases.
Higher commodity prices aided exports in 2021, and the trend is expected to continue in the first half of 2022 but may see some pressure in the second half as imports start picking up, estimates Schroders.
Consulting firm Asia Perspective in its investment outlook for Indonesia sees digital and green economy as key growth sectors. In 2021, the country surpassed Singapore as Southeast Asia’s most heavily invested digital economy, the consultancy firm’s outlook says. According to the latest SEA e-Conomy report by Google, Bain, and Temasek, Southeast Asia’s digital economy is expected to expand to $363 bn by 2025. Nearly half of the growth is expected to come from Indonesia.
Furthermore, Indonesia’s green economy is expected to take off this year with the electric vehicle (EV) industry playing a key role. In order to get more value from the nation’s rich abundance of resources, the Indonesian government introduced plans in 2019 to transform the country into a fully integrated EV battery hub – from mining to processing and recycling batteries. Indonesia is the world’s top nickel producer – the metal is a major component of EV batteries.
However, Indonesia faces limited access to green funding and technology transfer, according to Asia Perspective. “To tackle these challenges, the government strives to establish cross-border cooperation that could help Indonesia realize its transition to a green economy.” Multiple projects are set to develop this year.










 Australia
Australia China
China India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Japan
Japan Malaysia
Malaysia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam
 Germany
Germany Hong Kong
Hong Kong USA
USA Switzerland
Switzerland
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom








